What Are The Consumables Used In Filter Presses?
Filter presses consume several key consumables during operation. The quality and replacement frequency of these consumables directly affect the equipment’s operating efficiency, filtration performance, and service life. The following are the main consumables for filter presses.
Filter Cloth
The filter cloth acts as a filtration medium to achieve solid-liquid separation, with the filter cake retained on the surface of the filter cloth.
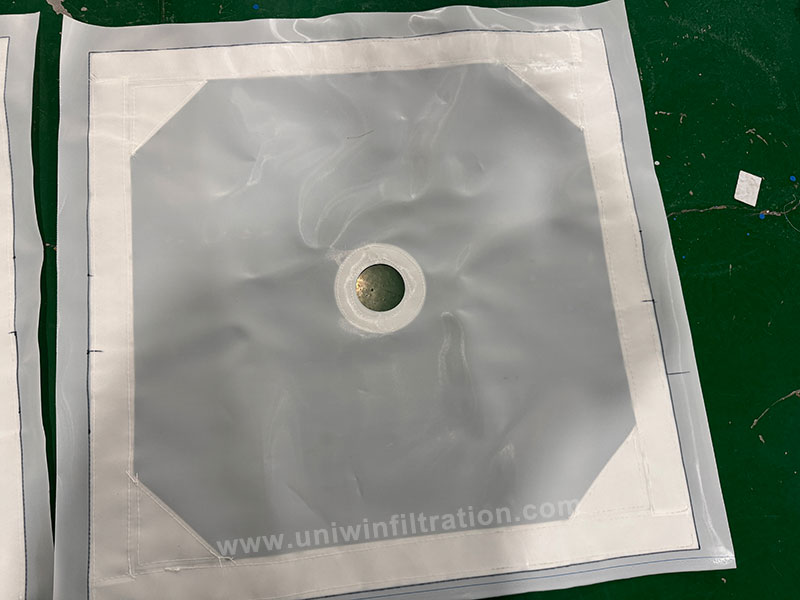
Common materials
- Polyester (PET): General-purpose, temperature resistance up to 130°C.
- Polypropylene (PP): Acid and alkali-resistant, economical and practical.
- Nylon (PA): Excellent wear resistance, suitable for high-pressure environments.
Forms of damage
- Surface clogging, reduced filtration efficiency.
- Edge wear, filter cake leakage.
- Reduced permeability, cloudy filtrate.
- Replacement Cycle: 3–12 months (depending on the material and workload)
Maintenance Suggestions
- Regular high-pressure cleaning to avoid grease residue.
- Avoid folding and crushing the filter cloth.
- Use neutral cleaning agents during cleaning, avoiding strong acids and alkalis.
Filter Plate
The main structural component of the filter chamber supports pressure and carries the filter cloth and filter cake.
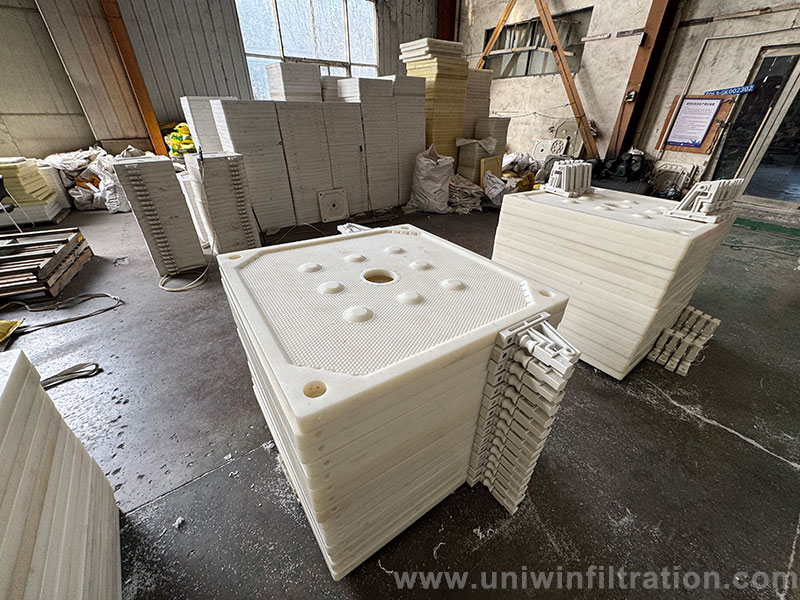

Types
- Standard Chamber Filter Plate
- Plate and Frame Filter Plate
- Diaphragm Filter Plate (with elastic diaphragm)
- Gasketed Filter Plate
Common materials
- Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight and corrosion-resistant;
- Cast Iron/Stainless Steel: For high pressure and heavy loads;
- High-performance composite materials: Suitable for special industries (such as high-temperature environments).
Causes of damage
- Overpressure deformation.
- The filter cloth carrying debris impacts the filter plate.
- Filter plate cracks and fractures.
- Service Life: 2–5 years
Precautions
- Regularly check for leaks.
- Replace deformed filter plates immediately.
- Using an automatic plate-pulling device can reduce wear and tear.
Filter Plate Handle
Guides the filter plate to slide smoothly in the guide rails, facilitating manual or automatic plate pulling.
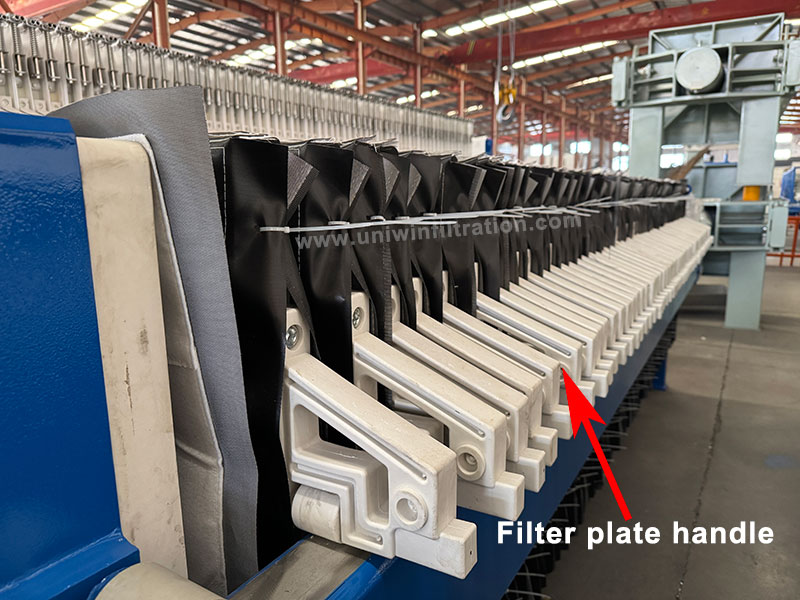

Material types
- Nylon: Wear-resistant, smooth sliding.
- Polypropylene (PP): Low cost, acid and alkali-resistant.
- Metal-coated: Used for heavy-duty filter presses.
Signs of damage
- Severe wear, causing the filter plate to jam during sliding.
- Loose screws, causing the filter plate to fall or slip off.
- Broken handle, causing automatic plate pulling malfunction.
- Replacement Cycle: 6–12 months (depending on usage frequency)
Recommendations
- Regularly lubricate the guide rails.
- Check for loose screws and tighten them promptly.
- Purchase handles in bulk for uniform replacement.
Hydraulic Oil
Drives the filter plates to clamp/unclamp, supporting the normal operation of the hydraulic system.
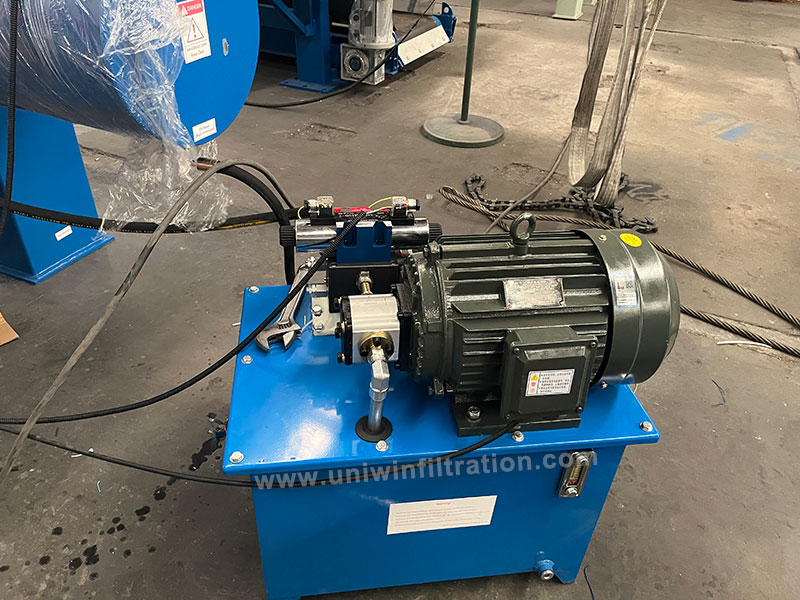

Types
- Anti-wear hydraulic oil;
- Synthetic hydraulic oil (for high-temperature environments);
- Food-grade hydraulic oil (for the food industry).
Signs of contamination
- Darkening of color
- Unusual odor or sediment
- Fluctuations in system pressure
- Replacement Cycle: Every 2000 operating hours or once a year
Usage recommendations
- Regularly check the oil level and oil quality.
- When replacing hydraulic oil, the oil filter should also be replaced.
- If there is water in the hydraulic system, the machine should be stopped for maintenance.
Hydraulic Seals (Cylinder Seals, O-rings)
To maintain the seal of the hydraulic system and prevent oil leakage and pressure loss.
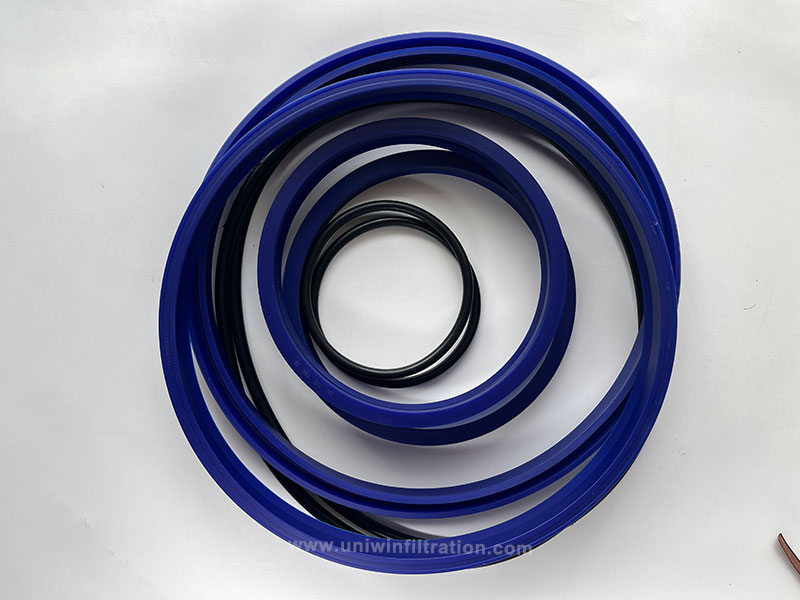

Materials
Polyurethane, nitrile rubber, PTFE, etc.;
Wear and tear issues
- Seal hardening, oil leakage.
- Damaged oil scraper ring, cylinder contamination.
- Unstable pressure, sluggish operation.
- Replacement Cycle: 6–24 months (depending on hydraulic cylinder load)
Usage recommendations
- Maintain the cleanliness of the hydraulic oil.
- If frequent oil dripping or pressure loss occurs, the seals should be checked first.
Conclusion
Filter presses involve various critical consumables during long-term operation, and the performance and condition of each consumable directly affect the filtration efficiency and stability of the equipment. Proper selection, regular maintenance, and timely replacement of these consumables are core strategies for ensuring efficient operation and extending the service life of the filter press.
